
你好,我是黄申。
“田忌赛马”的故事我想你肯定听过吧?田忌是齐国有名的将领,他常常和齐王赛马,可是总是败下阵来,心中非常不悦。孙膑想帮田忌一把。他把这些马分为上、中、下三等。他让田忌用自己的下等马来应战齐王的上等马,用上等马应战齐王的中等马,用中等马应战齐王的下等马。三场比赛结束后,田忌只输了第一场,赢了后面两场,最终赢得与齐王的整场比赛。
孙膑每次都从田忌的马匹中挑选出一匹,一共进行三次,排列出战的顺序。是不是感觉这个过程很熟悉?这其实就是数学中的排列过程。
我们初高中的时候,都学过排列,它的概念是这么说的:从n个不同的元素中取出m(1≤m≤n)个不同的元素,按照一定的顺序排成一列,这个过程就叫排列(Permutation)。当m=n这种特殊情况出现的时候,比如说,在田忌赛马的故事中,田忌的三匹马必须全部出战,这就是全排列(All Permutation)。
如果选择出的这m个元素可以有重复的,这样的排列就是为重复排列(Permutation with Repetition),否则就是不重复排列(Permutation without Repetition)。
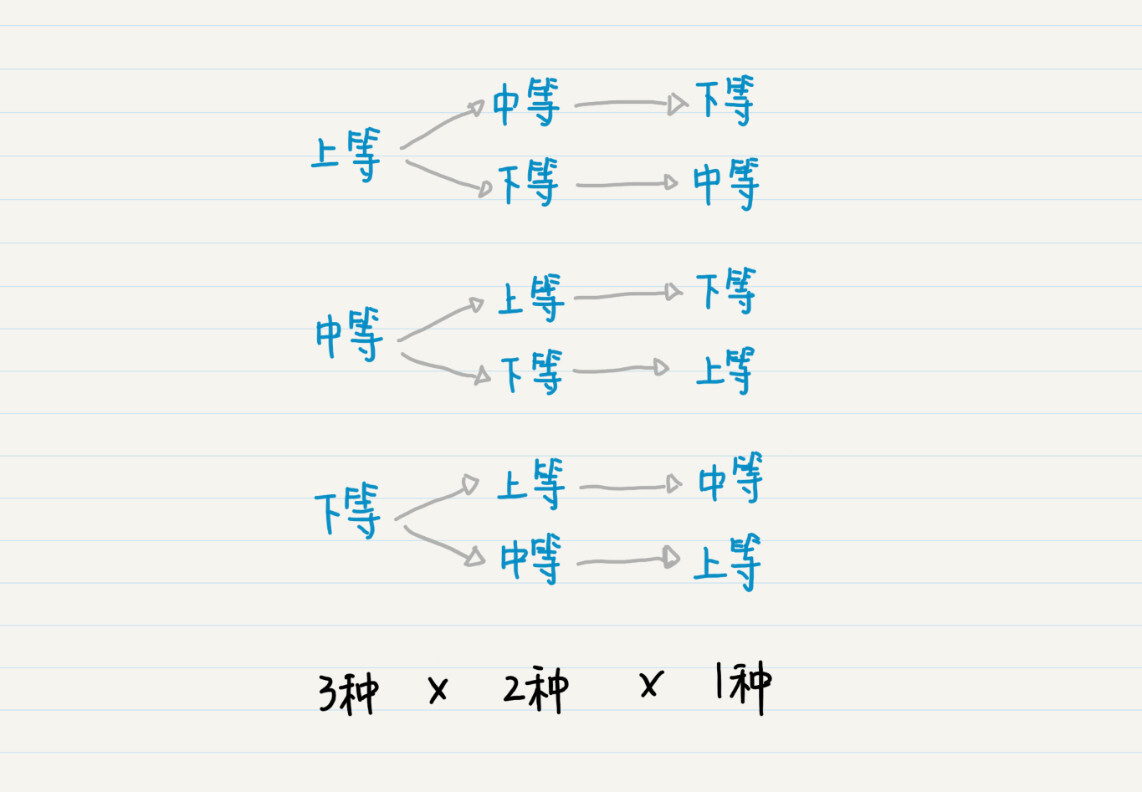
看出来没有?这其实是一个树状结构。从树的根结点到叶子结点,每种路径都是一种排列。有多少个叶子结点就有多少种全排列。从图中我们可以看出,最终叶子结点的数量是3x2x1=6,所以最终排列的数量为6。
{上等,中等,下等}
{上等,下等,中等}
{中等,上等,下等}
{中等,下等,上等}
{下等,上等,中等}
{下等,中等,上等}
我用t1,t2和t3分别表示田忌的上、中、下等马跑完全程所需的时间,用q1,q2和q3分别表示齐王的上、中、下等马跑全程所需的时间,因此,q1<t1<q2<t2<q3<t3。
如果你将这些可能的排列,仔细地和齐王的上等、中等和下等马进行对比,只有{下等,上等,中等}这一种可能战胜齐王,也就是t3>q1,t1<q2,t2<q3。
对于最终排列的数量,这里我再推广一下:
-
对于n个元素的全排列,所有可能的排列数量就是nx(n-1)x(n-2)x…x2x1,也就是n!;
-
对于n个元素里取出m(0<m≤n)个元素的不重复排列数量是nx(n-1)x(n-2)x…x(n - m + 1),也就是n!/(n-m)!。
这两点都是可以用数学归纳法证明的,有兴趣的话你可以自己尝试一下。
如何让计算机为田忌安排赛马?
我们刚才讨论了3匹马的情况,这倒还好。可是,如果有30匹马、300匹马,怎么办?30的阶乘已经是天文数字了。更糟糕的是,如果两组马之间的速度关系也是非常随机的,例如q1<q2<t1<t2<q3<t3, 那就不能再使用“最差的马和对方最好的马比赛”这种战术了。这个时候,人手动肯定是算不过来了,计算机又要帮我们大忙啦!我们使用代码来展示如何生成所有的排列。
如果你细心的话,就会发现在新版舍罕王赏麦的案例中,其实已经涉及了排列的思想,不过那个案例不是以“选取多少个元素”为终止条件,而是以“选取元素的总和”为终止条件。尽管这样,我们仍然可以使用递归的方式来快速地实现排列。
不过,要把田忌赛马的案例,转成计算机所能理解的内容,还需要额外下点功夫。
首先,在不同的选马阶段,我们都要保存已经有几匹马出战、它们的排列顺序、以及还剩几匹马没有选择。我使用变量result来存储到当前函数操作之前,已经出战的马匹及其排列顺序。而变量horses存储了到当前函数操作之前,还剩几匹马还没出战。变量new_result和rest_horses是分别从result和horses克隆而来,保证不会影响上一次的结果。
其次,孙膑的方法之所以奏效,是因为他看到每一等马中,田忌的马只比齐王的差一点点。如果相差太多,可能就会有不同的胜负结局。所以,在设置马匹跑完全程的时间上,我特意设置为q1<t1<q2<t2<q3<t3,只有这样才能保证计算机得出和孙膑相同的结论。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Lesson7_1 {
// 设置齐王的马跑完所需时间
public static HashMap<String, Double> q_horses_time = new HashMap<String, Double>(){
{
put("q1", 1.0);
put("q2", 2.0);
put("q3", 3.0);
}
};
// 设置田忌的马跑完所需时间
public static HashMap<String, Double> t_horses_time = new HashMap<String, Double>(){
{
put("t1", 1.5);
put("t2", 2.5);
put("t3", 3.5);
}
};
public static ArrayList<String> q_horses = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("q1", "q2", "q3"));
/**
* @Description: 使用函数的递归(嵌套)调用,找出所有可能的马匹出战顺序
* @param horses-目前还剩多少马没有出战,result-保存当前已经出战的马匹及顺序
* @return void
*/
public static void permutate(ArrayList<String> horses, ArrayList<String> result) {
// 所有马匹都已经出战,判断哪方获胜,输出结果
if (horses.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(result);
compare(result, q_horses);
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < horses.size(); i++) {
// 从剩下的未出战马匹中,选择一匹,加入结果
ArrayList<String> new_result = (ArrayList<String>)(result.clone());
new_result.add(horses.get(i));
// 将已选择的马匹从未出战的列表中移出
ArrayList<String> rest_horses = ((ArrayList<String>)horses.clone());
rest_horses.remove(i);
// 递归调用,对于剩余的马匹继续生成排列
permutate(rest_horses, new_result);
}
}
}
另外,我还使用了compare的函数来比较田忌和齐王的马匹,看哪方获胜。
public static void compare(ArrayList<String> t, ArrayList<String> q) {
int t_won_cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(t_horses_time.get(t.get(i)) + " " + q_horses_time.get(q.get(i)));
if (t_horses_time.get(t.get(i)) < q_horses_time.get(q.get(i))) t_won_cnt ++;
}
if (t_won_cnt > (t.size() / 2)) System.out.println("田忌获胜!");
else System.out.println("齐王获胜!");
System.out.println();
}
下面是测试代码。当然你可以设置更多的马匹,并增加相应的马匹跑完全程的时间。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> horses = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("t1", "t2", "t3"));
Lesson7_1.permutate(horses, new ArrayList<String>());
}
在最终的输出结果中,6种排列中只有一种情况是田忌获胜的。
[t3, t1, t2]
3.5 1.0
1.5 2.0
2.5 3.0
田忌获胜!
如果田忌不听从孙膑的建议,而是随机的安排马匹出战,那么他只有1/6的获胜概率。
说到这里,我突然产生了一个想法,如果齐王也是随机安排他的马匹出战顺序,又会是怎样的结果?如果动手来实现的话,大体思路是我们为田忌和齐王两方都生成他们马匹的全排序,然后再做交叉对比,看哪方获胜。这个交叉对比的过程也是个排列的问题,田忌这边有6种顺序,而齐王也是6种顺序,所以一共的可能性是6x6=36种。
我用代码模拟了一下,你可以看看。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> t_horses = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("t1", "t2", "t3"));
Lesson7_2.permutate(t_horses, new ArrayList<String>(), t_results);
ArrayList<String> q_horses = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("q1", "q2", "q3"));
Lesson7_2.permutate(q_horses, new ArrayList<String>(), q_results);
System.out.println(t_results);
System.out.println(q_results);
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < t_results.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < q_results.size(); j++) {
Lesson7_2.compare(t_results.get(i), q_results.get(j));
}
}
}
由于交叉对比时只需要选择2个元素,分别是田忌的出战顺序和齐王的出战顺序,所以这里使用2层循环的嵌套来实现。从最后的结果可以看出,田忌获胜的概率仍然是1/6。
暴力破解密码如何使用排列思想?
聊了这么多,相信你对排列有了更多了解。在概率中,排列有很大的作用,因为排列会帮助我们列举出随机变量取值的所有可能性,用于生成这个变量的概率分布,之后在概率统计篇我还会具体介绍。此外,排列在计算机领域中有着很多应用场景。我这里讲讲最常见的密码的暴力破解。
我们先来看去年网络安全界的两件大事。第一件发生在2017年5月,新型“蠕虫”式勒索病毒WannaCry爆发。当时这个病毒蔓延得非常迅速,电脑被感染后,其中的文件会被加密锁住,黑客以此会向用户勒索比特币。第二件和美国的信用评级公司Equifax有关。仅在2017年内,这个公司就被黑客盗取了大约1.46亿用户的数据。
看样子,黑客攻击的方式多种多样,手段也高明了很多,但是窃取系统密码仍然是最常用的攻击方式。有时候,黑客们并不需要真的拿到你的密码,而是通过“猜”,也就是列举各种可能的密码,然后逐个地去尝试密码的正确性。如果某个尝试的密码正好和原先管理员设置的一样,那么系统就被破解了。这就是我们常说的暴力破解法。
我们可以假设一个密码是由英文字母组成的,那么每位密码有52种选择,也就是大小写字母加在一起的数量。那么,生成m位密码的可能性就是52^m种。也就是说,从n(这里n为52)个元素取出m(0<m≤n)个元素的可重复全排列,总数量为n^m。如果你遍历并尝试所有的可能性,就能破解密码了。
不过,即使存在这种暴力法,你也不用担心自己的密码很容易被人破解。我们平时需要使用密码登录的网站或者移动端App程序,基本上都限定了一定时间内尝试密码的次数,例如1天之内只能尝试5次等等。这些次数一定远远小于密码排列的可能性。
这也是为什么有些网站或App需要你一定使用多种类型的字符来创建密码,比如字母加数字加特殊符号。因为类型越多,n^m中的n越大,可能性就越多。如果使用英文字母的4位密码,就有52^4=7311616种,超过了700万种。如果我们在密码中再加入0~9这10个阿拉伯数字,那么可能性就是62^4=14776336种,超过了1400万。
同理,我们也可以增加密码长度,也就是用n^m中的m来实现这一点。如果在英文和阿拉伯数字的基础上,我们把密码的长度增加到6位,那么就是62^6=56800235584种,已经超过了568亿了!这还没有考虑键盘上的各种特殊符号。有人估算了一下,如果用上全部256个ASCII码字符,设置长度为8的密码,那么一般的黑客需要10年左右的时间才能暴力破解这种密码。
小结
排列可以帮助我们生成很多可能性。由于这种特性,排列最多的用途就是穷举法,也就是,列出所有可能的情况,一个一个验证,然后看每种情况是否符合条件的解。
古代的孙膑利用排列的思想,穷举了田忌马匹的各种出战顺序,然后获得了战胜齐王的策略。现代的黑客,通过排列的方法,穷举了各种可能的密码,试图破坏系统的安全性。如果你所面临的问题,它的答案也是各种元素所组成的排列,那么你就可以考虑,有没有可能排列出所有的可能性,然后通过穷举的方式来获得最终的解。

思考题
假设有一个4位字母密码,每位密码是a~e之间的小写字母。你能否编写一段代码,来暴力破解该密码?(提示:根据可重复排列的规律,生成所有可能的4位密码。)
欢迎在留言区交作业,并写下你今天的学习笔记。你可以点击“请朋友读”,把今天的内容分享给你的好友,和他一起精进。

精选留言
classes = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
def get_password(n, result = ''):
if n == 0:
if result == password:
print(password)
else:
for i in classes:
new_result = copy.copy(result)
new_result = new_result + i
get_password(n - 1, new_result)
get_password(6)
/** permutaion: 排列。
* 从n个数中选出m个数的方式,若不考虑顺序Cn(m),若考虑顺序An(m)
*/
/* 问题:密码排列
* 假设有一个 4 位字母密码,每位密码是 a~e 之间的小写字。
* 编写密码可能排列方式。
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Permutation {
private:
int resultCount_ = 0;
public:
/** Details: 根据输入字母列表,获得所有的排列方式。
* params: result- 当前排列形式, candidate- 未排列字母表。
* return: null
*/
void breakPassword(vector<string> result, vector<string> candidate) {
int len = candidate.size();
if (0 == len) {
// 无字母剩余,输出排列结果
outputResult(result);
resultCount_++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
vector<string> resultNew;
vector<string> candidateLeft;
// 读取排列字母
resultNew = result;
resultNew.push_back(candidate[i]);
// 获得剩余字母表
candidateLeft = candidate;
vector<string>::iterator it = candidateLeft.begin();
candidateLeft.erase(it + i);
// 递归
breakPassword(resultNew, candidateLeft);
}
}
// 输出结果
void outputResult(vector<string> result) {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
// 获得所有可能密码总数
int getResultCount() {
return resultCount_;
}
};
int main(void) {
vector<string> fourAlphabetString = {"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"};
vector<string> res;
Permutation test;
test.breakPassword(res, fourAlphabetString);
cout << "可能的密码形式:";
cout << test.getResultCount() << "种" << endl;
}
一、田忌和齐王双方都随机选择马匹出战顺序
import copy
# 设置齐王的马跑完所需时间
q_horses_time = {"q1": 1.0, "q2": 2.0, "q3": 3.0}
# 设置田忌的马跑完所需时间
t_horses_time = {"t1": 1.5, "t2": 2.5, "t3": 3.5}
# 双方均随机选择出战的马匹
q_horses = ["q1", "q2", "q3"]
t_horses = ["t1", "t2", "t3"]
def permutation(horses, result=None, all_results=None):
"""
使用函数的递归(嵌套)调用,找出所有可能的马匹出战顺序
:param all_results: 马匹出战顺序的所有排列(全排列)
:param horses: 目前还剩多少马没有出战
:param result: 保存当前已经出战的马匹及顺序(其中一种排列)
:return:
"""
if result is None:
result = []
if all_results is None:
all_results = []
# 所有马匹都已经出战,返回出战顺序
if len(horses) == 0:
all_results.append(result)
return
for k in range(len(horses)):
# 从剩下的未出战马匹中 选择一匹 加入结果
new_result = copy.copy(result)
new_result.append(horses[k])
# 将已选择的马匹从未出战的列表中移除
rest_horses = copy.copy(horses)
rest_horses.pop(k)
# 递归调用 对于剩余的马匹继续生成排列
permutation(rest_horses, new_result, all_results)
return all_results
def compare(t, q):
t_won_cnt = 0
for m in range(len(t)):
print(str(t_horses_time.get(t[m])) + ',' + str(q_horses_time.get(q[m])))
if t_horses_time.get(t[m]) < q_horses_time.get(q[m]):
t_won_cnt = t_won_cnt + 1
if t_won_cnt > len(t)//2:
print("田忌获胜!")
else:
print("齐王获胜!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 双方均随机安排马匹出战,田忌获胜的概率仍为 1/6
t_results = permutation(t_horses)
q_results = permutation(q_horses)
print(t_results)
print(q_results)
for i in range(len(t_results)):
for j in range(len(q_results)):
compare(t_results[i], q_results[j])
-------------------------代码-----------------------------------
/**
* 排列
*
* @param passwords 待排列的字符
* @param results 排列的结果
***/
public void range(ArrayList<String> passwords, ArrayList<String> results) {
//如果为空则不需要排列
if (passwords.isEmpty()) {
String collect = String.join("", results);
System.out.print(collect + "\t");
}
for (int i = 0; i < passwords.size(); i++) {
String password = passwords.get(i);
ArrayList<String> newResult = (ArrayList<String>) results.clone();
ArrayList<String> newPassword = (ArrayList<String>) passwords.clone();
newResult.add(password);
newPassword.remove(i);
range(newPassword,newResult);
}
}
public class L7_2 {
public static void calLetterList(ArrayList<String> l, ArrayList<String> result) {
if (result.size() == l.size()) {
System.out.println(result);
return;
}
for (String letter : l) {
ArrayList<String> newResult = (ArrayList<String>) result.clone();
newResult.add(letter);
calLetterList(l, newResult);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> l = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d", "e"));
calLetterList(l, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using std::string;
using namespace std;
void BreakPassword( string Words, int PasswordLen, string result)
{
if (result.length() == PasswordLen)
{
//C++中string类型不能直接输出,需加头问题#include<string>,不能用#include<string.h>
cout << result << " ";
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < Words.length(); ++i)
{
string newResult = result;
newResult.insert( newResult.end(), Words[i] );
BreakPassword(Words, PasswordLen, newResult);
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int passwordLen = 4;
string words("abcde");
string result = "";
BreakPassword(words, passwordLen, result);
return 0;
}
static char[] pwdcs = new char[] { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' };
static String[] crack(int len) {
String[] ps = new String[] { "" };
while (len-- > 0) {
String[] nps = new String[ps.length * pwdcs.length];
int nsbsi = 0;
for (String pwd : ps) {
for (char c : pwdcs) {
nps[nsbsi++] = pwd + c;
}
}
ps = nps;
}
return ps;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] pwds = crack(4);
for (String pwd : pwds) {
System.out.println(pwd);
}
/**
* 输出结果
* aaaa
* aaab
* aaac
* aaad
* aaae
* aaba
* ....
* 省略517行
* ....
* eeed
* eeee
*
*/
}
}
package main
import "fmt"
var option = []string{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"}
func main() {
var password [4]string
passwdGen(4, password)
}
// 最简单的情形就是只有密码只有1位,通过控制密码的位数,降低问题的规模
func passwdGen(length int, password [4]string) {
if length == 0 {
fmt.Println(password)
return
} else {
password := password
for _, val := range option {
password[length-1] = val
passwdGen(length-1, password)
}
}
}
```
二、思考题:
import copy
my_pwd = 'bada' # 实际密码
pwd_char = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] # 字符数组
def decrypt(char, password=None):
"""
使用函数的递归(嵌套)调用,找出所有可能的 4 位密码
:param char: 组成密码的字符
:param password: 当前找出的密码
:return:
"""
if password is None:
password = []
if len(password) == 4:
if "".join(password) == my_pwd:
print(password)
print("密码破解成功!")
return True
else:
return False
for i in range(len(char)):
new_password = copy.copy(password)
new_password.append(char[i])
rest_char = copy.copy(char)
if decrypt(rest_char, new_password):
return True
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
decrypt(pwd_char)
a = ['a','b','c','d','e']
password = 'abcd'
f=''
for i in password:
for n in a:
if n == i:
f+=i
print('f=',f)
dict = ["a","b","c","d","e"]
origPsw = "caaeeae"
def calcPsw(count,res):
\t if (count <= 0):
\t\t if(res==origPsw):
\t\t\t print("password:"+res)
\t\t return
\t c = count-1
\t for i in dict:
\t\t newRes = res+i
\t\t calcPsw(c,newRes)
calcPsw(7,"")
LETTERS = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
def all_passwords():
last_passwords = [[]]
for i in range(4):
new_passwords = []
for password in last_passwords:
for letter in LETTERS:
new_password = password + [letter]
new_passwords.append(new_password)
last_passwords = new_passwords
return last_passwords
/**
* a~e 区间 4位密码重复排列[PHP版]
* 625个
*/
class Lession7_test
{
public function __construct()
{
$this->permutate(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'], '');
}
public function permutate($letters, $result)
{
if (strlen($result) == 4) {
echo $result."\n";
return ;
}
for($i = 0; $i < count($letters); $i++) {
$new_result = $result;
$new_result .= $letters[$i];
$this->permutate($letters, $new_result);
}
}
}
$Lession7_4 = new Lession7_test();
var result = []
function getPassword(passwordChars, num, password) {
if (num == 0) {
return result.push(password)
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < passwordChars.length; i++) {
getPassword(passwordChars, num - 1, password + passwordChars[i])
}
}
}
getPassword(chars, 4, '')
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] passwordCharts= {'a','b','c','d','e'};
getPassword(passwordCharts,4,"");
}
public static void getPassword(char[] passwdChars,int num,String pwd){
if(num == 0){
System.out.println(pwd);
return;
}
for(int i = 0 ;i < passwdChars.length;i ++){
String pwdNew = pwd + passwdChars[i];
getPassword(passwdChars,num-1,pwdNew);
}
}